What to Look for in July
The scorpion’s star clusters, and Mars reveals elusive Uranus
Follow the tail of Scorpius to locate star clusters M6 and M7, let Mars guide you to observe planet Uranus, and see the Moon gather a group of planets in the morning.
Highlights
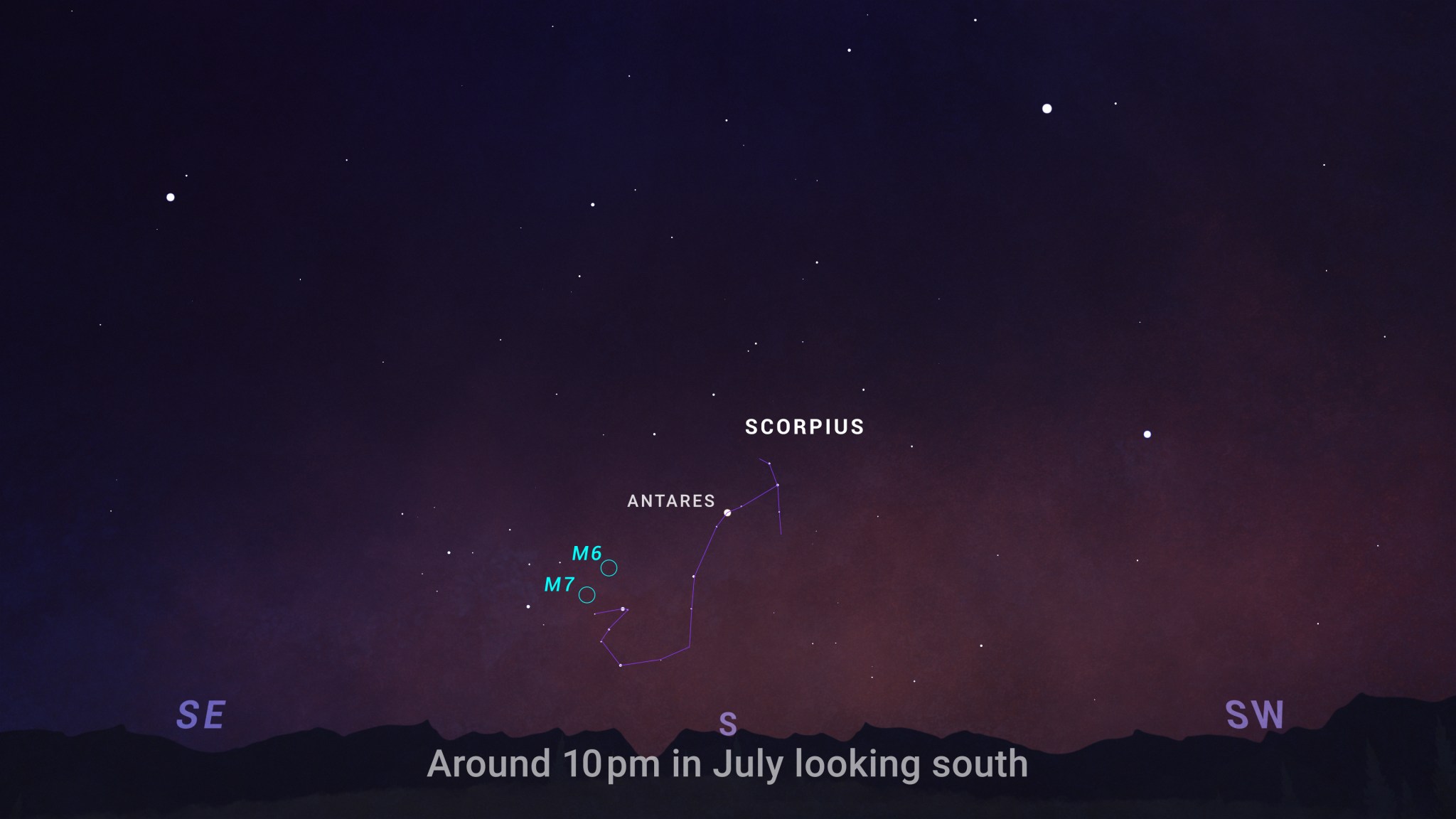
- All month – Two easy-to-spot star clusters – M7, aka Ptolemy’s Cluster, and M6, the Butterfly Cluster – are both located about 5 degrees east of the the bright stars that mark the “stinger” end of the scorpion’s tail. They reach their highest point in the sky around 10 or 11 pm local time.
- July 2 & 3 – The crescent Moon will join Jupiter and Mars in the east before sunrise. Looking for them before the sky starts to brighten, you’ll also find the Pleiades star cluster above Jupiter, and bright stars Capella and Aldebaran nearby.
- July 5 – New moon
- July 7 & 8 – Those with an unobstructed view of the western horizon can spot Mercury shining brightly, low in the sky with a slim crescent Moon. Look for them starting 30 to 45 minutes after the Sun sets.
- July 13 – For the first few hours after dark, look to the southwest to find the first-quarter Moon snuggled up to bright bluish-white star Spica. For much of the lower 48 U.S. and most of Mexico, the Moon will appear to pass in front of Spica – an event called an occultation. Check your favorite skywatching app for the view from your location.
- July 14-16 – Grab your binoculars and have a look at Mars in the early morning before the sky starts to brighten, and you’ll find the distant planet Uranus quite close by.
- July 21 – Full moon
- July 30 – Look for a close gathering of Jupiter, Mars, and the Moon with the bright stars of the constellation Taurus in the a.m. sky before dawn.
Transcript
What’s Up for July? The Moon gets the band back together, find planet Uranus with some help from Mars, and the star clusters that feel the Scorpion’s sting.
All month in July, as in June, the planetary action is in the a.m. sky. Find Saturn rising around midnight, and climbing high into the south by sunrise. Mars rises a couple of hours later, with Jupiter trailing behind it, and shifting higher in the sky each day.
On July 2nd and 3rd before sunrise, the crescent Moon will join Jupiter and Mars in the east. Looking for them before the sky starts to brighten, you’ll also find the Pleiades star cluster above Jupiter, as well as bright stars Capella and Aldebaran.
As the Moon swings around the planet in its orbit, this same group gets back together at the end of the month, but as a much tighter gathering of Jupiter, Mars, and the Moon with the bright stars of the constellation Taurus.
Then on the evening of July 7th and 8th, those with an unobstructed view of the western horizon can spot Mercury shining brightly, low in the sky with a slim crescent Moon. Look for them starting 30 to 45 minutes after the Sun sets. Observers in the Southern Hemisphere will find Mercury a good bit higher in the northwest sky all month after sunset.
On July 13, for the first few hours after dark, look to the southwest to find the first quarter Moon snuggled up to bright bluish-white star Spica. For much of the lower 48 United States and most of Mexico, the Moon will appear to pass in front of Spica – an event called an occultation.
Next, over three days in mid-July, grab your binoculars and have a look at Mars in the early morning before the sky starts to brighten, and you’ll find the distant planet Uranus quite close by. Uranus is not too difficult to see with binoculars or a small telescope anytime it’s reasonably high above the horizon at night, but you really need to know where to look for it, or use an auto-guided telescope. But occasionally the Moon or one of the brighter planets will pass close to Uranus in the sky, making for a great opportunity to find it with ease.
The winding form of constellation Scorpius, adorned with the bright red star Antares, is a feature of the night sky around the world this time of year. And at the tip of the scorpion’s tail are two well-known star clusters that are well placed for viewing at this time of year.
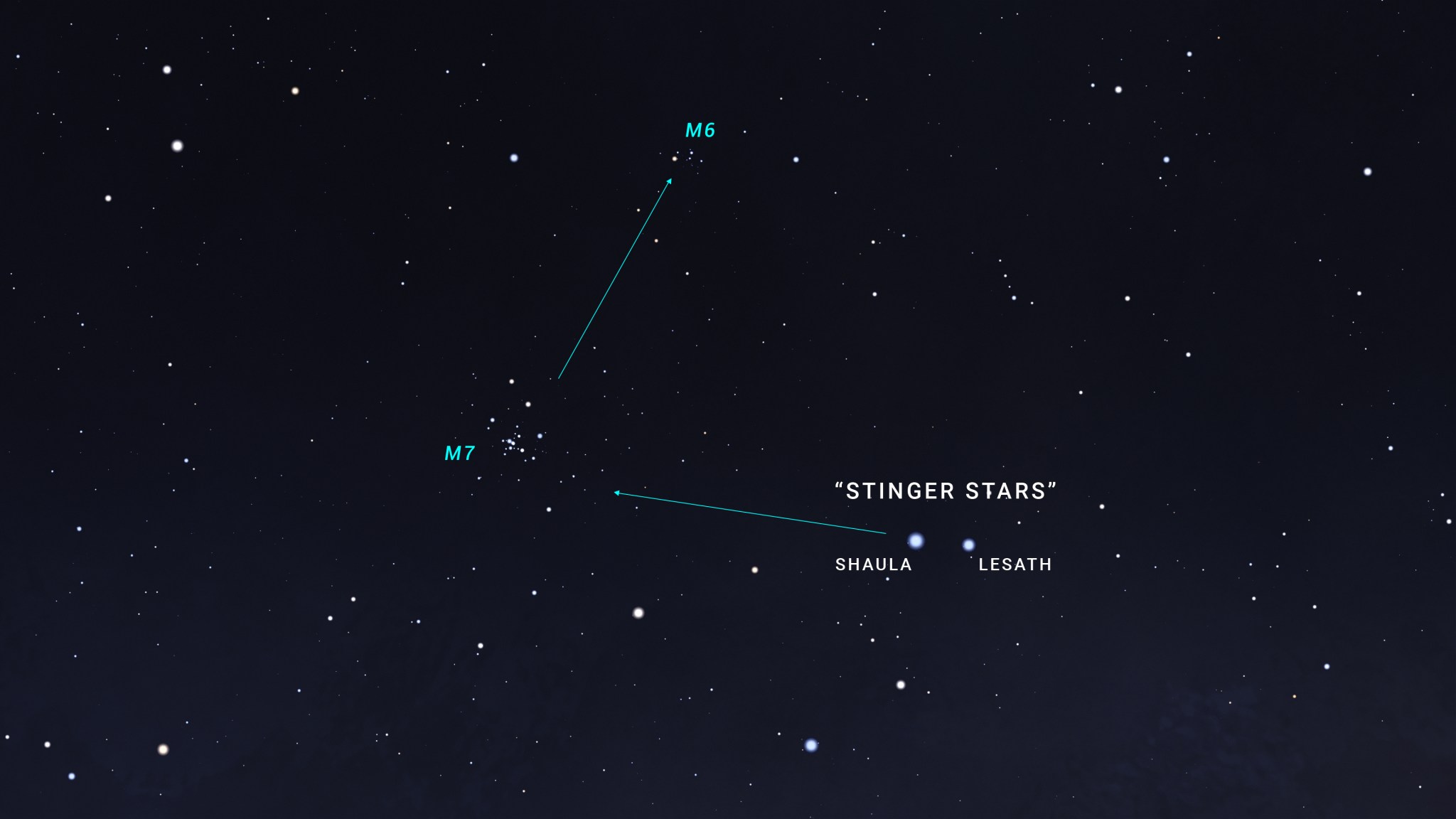
M7, aka Ptolemy’s Cluster, and M6, the Butterfly Cluster, are both located about 5 degrees east of the the bright stars that mark the “stinger” end of the scorpion’s tail. They reach their highest point in the sky around 10 or 11 pm local time.
To find M7, imagine a line toward the east through the “stinger stars,” Lesath and Shaula, and it will lead you straight to the star cluster. M6 is just a couple of degrees above M7. Both are “open star clusters,” meaning they’re loose groupings of stars that formed together, in the same region of space, and they’re only loosely bound together by gravity, so they’ll eventually go their separate ways.
M7 is just visible to the unaided eye under dark skies as a hazy patch just left of the tip of the scorpion’s tail. But it’s best seen with binoculars or a telescope with a wide field of view. Its stars are located at a distance of about 1000 light years from us, and they formed about 200 million years ago. The cluster was discovered by Greek-Roman astronomer Ptolemy in the year 130, hence its other name.
M6 is about half the apparent size of M7, and contains fewer stars. It’s also a bit farther away from us, at around 1600 light years. It’s estimated to be about half as old as M7, at an age of around 100 million years. It was discovered by Italian astronomer and contemporary of Galileo, Giovanni Battista Hodierna, in 1654.
These two clusters are easy to observe in July, and their location in Scorpius makes them pretty straightforward to locate on a clear night.
So there’s no reason to fear of this scorpion’s sting. Instead, let it guide you to two distant star clusters, and see for yourself two little families of stars in the process of spreading out into the Milky Way.
Here are the phases of the Moon for July.
Stay up to date on NASA’s missions exploring the solar system and beyond at science.nasa.gov. I’m Preston Dyches from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and that’s What’s Up for this month.
Skywatching Resources
About the ‘What’s Up’ Production Team
“What’s Up” is NASA’s longest running web video series. It had its first episode in April 2007 with original host Jane Houston Jones. Today, Preston Dyches, Christopher Harris, and Lisa Poje are the space enthusiasts who produce this monthly video series at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Additional astronomy subject matter guidance is provided by JPL’s Bill Dunford, Gary Spiers, Lyle Tavernier, and the Night Sky Network’s Kat Troche.